Active Assailant Attacks: Lockdown
Lockdown!, Lockdown!, Lockdown!
Three words you never want to hear in a row – but ones you need to plan for well in advance. We believe the phase “Lockdown” should be a universal call to action – which has different actions, depending on where you are and where the threat is. Similar to a fire or chemical spill within (or near) a commercial high-rise office building, there may be some places where it is safer to shelter-in-place and some where it is safer to evacuate. But unlike those and any other threats – there may be a moment/place/time when you are confronted directly by the active assailant – with “no where to run and no where to hide” (apologies to Holland, Dozier and Holland) – and you will have to fight to defend your own life and maybe the lives of others.
A Lockdown should be different from a Secure and Hold. A Secure and Hold order is when the Active Assailant is near your location, but not (yet!) a direct threat to you. When a building or a school goes on Secure and Hold, it should mean that the threat is not on campus and no one goes in and no one comes out (except as authorized by emergency services). Secure and Hold orders can become Lockdowns, when the threat does move to your building. This may happen very quickly – and if it does, try to get the words “Lockdown, Lockdown, Lockdown” out over public address systems, text messages targeted to people in the building, etc. Also any info which can help identify the attacker(s); the more intelligence provided, the better – such has what the attacker(s) look like, weapons, which entrance they came in, where they might be now, etc. We encourage the three calls of the word “Lockdown!” back to back, this way it is very distinctive, and in case someone missed hearing the word “Lockdown” the first time. And by the way, there is no reason not to keep announcing where the threat is located – only if you are in a safe place to do so. Offsite security/law enforcement teams who have access to your public address system and/or text alert system can perform this as well. Note, we do recommend that cell phones be put on silent when you are temporarily ‘hiding’ or denying access, in a safer location – and those folks should remain quiet to avoid directing the attacker to their location.
Think of this threat, like it’s radioactive. If you heard there was a briefcase full of radioactive material in the lobby of your building, you would want to get as far away from it, as quickly as possible. So, for two of the three actions (evacuation and sheltering in place) associated with a Lockdown, look to limit your time near the threat, increase the distance from the threat, and use shielding from the threat:
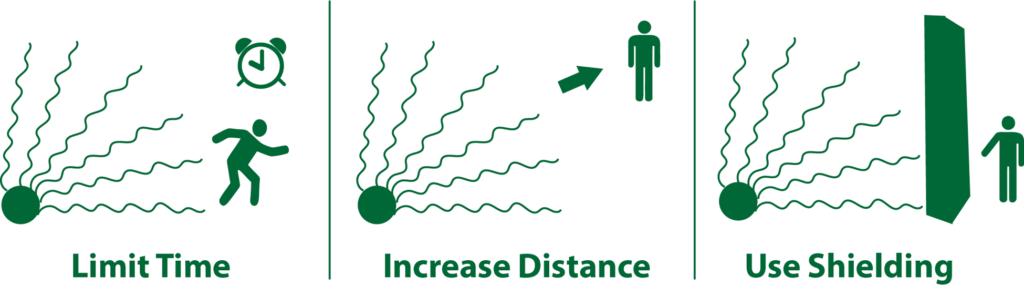
Run/Avoid – Add Time and Distance from the Threat
This is shorthand for evacuate away from the threat to a safer area until the situation is ended; and let your team or emergency responders know of your location and status. That includes a very important checklist point to “running/avoiding” away from an Active Assailant (or any other threat where you are evacuating): Accountability. Please let your supervisor, or emergency action team leader know where you are and your status (injured, not injured, etc.) when you have moved to someplace safer.
If your office, school, work location, etc. has emergency assembly areas – use them when you are evacuating – even for Active Assailant Attacks. At least that’s the plan. If you escape out the back of the building towards the Assembly Point, and see there are other attackers there – well, then go somewhere else! That may mean back into the building. Every Emergency Action Plan should have multiple emergency assembly areas/points – including contingency ones if the primary ones are unsafe. This is a key element to Crisis Action Planning.
Hide/Deny – Add a layer of Shielding, until you can Escape or the Threat is Ended
Also shorthand for finding a safer place to be, one that provides Cover at best and Concealment at a minimum.
Fight/Defend
This is the tough one. Not something we recommend for people under 18 (K12 schools probably use a different protective methodology for Response by the public to an active assailant attack, such as A.L.I.C.E.). Here’s a really good video from the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) which sums up “Run, Hide, Fight” (Note: some may find this video disturbing or uncomfortable, watch at your own discretion and liability):
Active Assailant Attacks: Lockdown Read More »